HomePressure Converter
Pressure Conversion Calculator
From pascals to PSI, convert pressure in science, engineering, or daily life.Pressure Converter
Convert from
Convert to
**Formula:
Discover Other Unit Converters
Try Other Pressure Converters
Atmosphere to BarAtmosphere to MegapascalAtmosphere to Meters of waterAtmosphere to PascalAtmosphere to TorrBar to AtmosphereBar to MegapascalBar to Meters of waterBar to PascalBar to TorrHectopascal to AtmosphereHectopascal to BarHectopascal to MegapascalHectopascal to PascalInch mercury to Inch waterInch water to Pascal
Updated on December 1, 2025
Our pressure conversion calculator is a powerful online tool that helps you quickly convert between various pressure units like Pascal, bar, atmosphere, Torr, Centimeter mercury, and more. It’s designed to make conversions fast and accurate, with smart features such as real-time formula previews, adjustable decimal points, rounding modes, conversion history, and a built-in calculator. In this guide, I’ll explain the basics of pressure and show you how our pressure conversion calculator makes unit conversions simple, accurate, and efficient.About Our Pressure Conversion Calculator
Written By Nadiba Rahman
Nadiba Rahman
Reviewed by Mrinmoy Roy
Mrinmoy Roy
Share This Post
URL copied!
What Is Pressure?
Pressure refers to the force applied to a surface per unit area. For example, when you press your hand against a wall, the pressure is the force from your hand divided by the area it touches.The standard unit of pressure is the pascal (Pa). Other common units include pounds per square inch (psi), atmospheres (atm), and bar. Pressure measurements are important in fields like weather forecasting, marine navigation, and industrial work.
There are different types of pressure, such as surface pressure, fluid pressure, and gas (or vapor) pressure. Atmospheric pressure is measured with a barometer, while gas pressure is measured with a manometer. Many smartphones today have built-in barometers to measure air pressure, which can help detect weather changes or measure altitude.
How to Calculate Pressure?
The basic formula to calculate pressure is:P = F / A
Where P is the pressure, F is the force exerted, and A is the area over which the force is distributed.
In static fluids, pressure can be calculated using:P = ρgh
Where ρ is fluid density, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and h is the height of the fluid column.
Conversion Units of Our Pressure Converter
Below are the available units of pressure you can convert between using our pressure conversion calculator:- Atmosphere (atm): Atmosphere represents the average pressure at sea level. It is used in weather forecasting and general science.
- Bar: Frequently used in meteorology and fluid dynamics. 1 bar = 100,000 pascals (Pa).
- Centimeter of Mercury (cmHg): Often used in meteorology and medicine, particularly in blood pressure measurements.
- Centimeter of Water (cmH₂O): Often used in fluid dynamics and engineering to measure low pressures. 1 cmH₂O ≈ 98.1 pascals (Pa).
- Feet of Water (ftH₂O): Similar to cmH₂O but used in hydrology and engineering where large pressures are involved. 1 ftH₂O = 2,988.5 pascals (Pa).
- Hectopascal (hPa): Used in meteorology. 1 hectopascal = 100 pascals (Pa).
- Inch of Water (inH₂O): Typically used in HVAC systems and fluid dynamics to measure small pressures. 1 inch of water = 249.0889 pascals (Pa).
- Inch of Mercury (inHg): Commonly used in weather forecasting, altimetry, and aviation.
- Kilogram-force per Square Centimeter (kgf/cm²): It represents the pressure exerted by a kilogram of force applied to a square centimeter.
- Kilogram-force per Square Meter (kgf/m²): Used in fields like construction and fluid mechanics. 1 kgf/m² ≈ 98.07 pascals (Pa).
- Kilonewtons per Square Meter (kN/m²): Used in engineering and physics to measure pressure. 1 kN/m² = 1,000 pascals (Pa).
- Kilonewtons per Square Millimeter (kN/mm²): A unit for very high pressures, often used in materials science and engineering.
- Megapascal (MPa): Often used in materials science and high-pressure systems. 1 MPa = 1,000,000 pascals.
- Meters of Water (mH₂O): Commonly used in fluid dynamics and hydrology.
- Newton per Square Centimeter (N/cm²): 1 N/cm² = 10,000 pascals.
- Newton per Square Meter (N/m²): The SI unit for pressure, equivalent to pascal (Pa). 1 N/m² = 1 pascal.
- Newton per Square Millimeter (N/mm²): Used to measure very high pressures in materials science and mechanical engineering. 1 N/mm² = 1,000,000 pascals (Pa).
- Pascal (Pa): The SI unit of pressure, used universally in physics and engineering.
- Pound-force per Square Inch (lbf/in²): Used to measure tire pressure, hydraulic systems, and more.
- Pound-Force per Square Foot (lbf/ft²): 1 lbf/ft² = 47.8805 pascals (Pa).
- Tons per Square Foot (tn/ft²): Used in construction and engineering.
- Tons per Square Inch (tn/in²): Used for measuring high-pressure systems in engineering applications.
- Tonnes per Square Centimeter (t/cm²): This unit is used in some specialized industrial applications.
- Tonnes per Square Meter (t/m²): Used in construction and civil engineering to measure surface pressure.
- Torr (Torr): A unit of pressure used in vacuum systems and physics. 1 Torr = 1/760 of an atmosphere.
How Our Pressure Conversion Calculator Works?
Our pressure conversion calculator makes your pressure conversions easy from one unit to another. Here’s how it works:- Choose the pressure input and output pressure units you want to convert from and to.
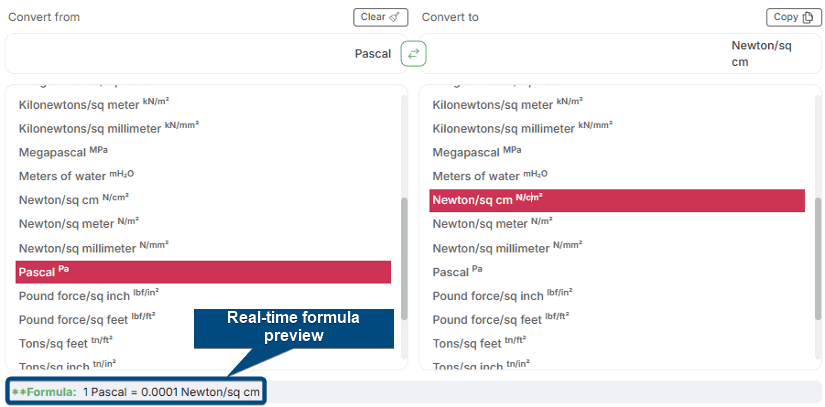
- Input the pressure value you want to convert.
- The calculator shows the converted result right away in the target unit. You can easily copy the result for your use.
Features of Our Pressure Conversion Calculator
Our pressure conversion calculator offers several easy-to-use features that make converting pressure units fast and accurate. All features are accessible in the settings menu, and the image below shows the default settings for each one.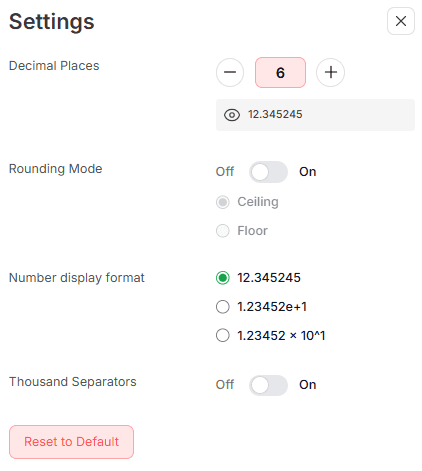
Adjustable Decimal Precision
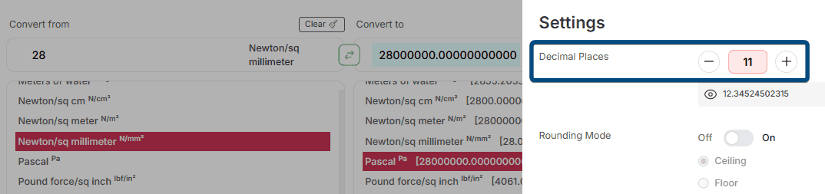
Precision is key in pressure calculations, especially for fluid mechanics, HVAC system testing, or industrial processes. A small change in decimal places can affect equipment calibration, safety margins, or product quality.That’s why we’ve included an adjustable decimal precision feature in our pressure converter. It lets you choose how detailed your result needs to be. The default is 6 decimal places, but you can adjust it from 0 to 12 for more precise or general results.
For example, 28 N/mm² to pascals with 11 decimal places will show 28000000.00000000000 Pa instead of just 28000000.000000 Pa, like the image below shows.
Rounding Mode Options
Even slight rounding differences can affect pressure distribution, equipment readings, or system stability. That’s why our calculator includes rounding mode control. It helps you to choose whether to round up, round down, or turn off the rounding altogether. This ensures your pressureconversion values match your project’s needs exactly and reduces errors during critical calculations.
Multiple Number Display Formats
Our calculator offers three number display formats:- Standard Decimal (e.g. 12.34524502)
- Scientific Notation (e.g. 1.2345245e+1)
- Engineering Format (e.g. 1.2345245 × 10^1)
For example, converting 1 bar to pascals shows 100,000 Pa in decimal format. When working with larger pressures like 1 megapascal (1,000,000 Pa), scientific notation (1.0e+6) or engineering format (1.0 × 10^6 Pa) makes the numbers easier to read and communicate.
Real-time Multi-unit Conversion
When you need to see the same pressure value in different units, converting them one by one can be slow and tiring. Our calculator’s real-time multi-unit conversion feature shows equivalent values in all other pressure units as soon as you enter a number.This saves time and helps you make quick decisions in experiments, system designs, or material tests.
Thousand Separators Toggle
Large pressure values can be difficult to read, and missing a single digit can cause significant calculation errors. Our calculator includes a thousand-separators toggle that adds commas to your numbers for better clarity.For example, 1234567 pascals (Pa) becomes 1,234,567 Pa, reducing errors and making it easier to review pressure data accurately.
Integrated Built-in Calculator
Suppose you need to adjust load factors or calculate fluid column pressures. Switching to a separate calculator just to do these quick math steps can be frustrating and slow you down.That’s why we built an integrated scientific calculator right into the tool. You can easily perform your calculations and send the result straight to the converter without hassle.
Easy Unit Swap
Sometimes you need to check conversions in both directions, like converting pascals (Pa) to atmospheres (atm), then back to pascals. Doing it manually can take time and lead to mistakes.Our one-click unit swap feature instantly switches the input and output units, so you can quickly double-check your work or view the conversion in reverse without any extra effort.
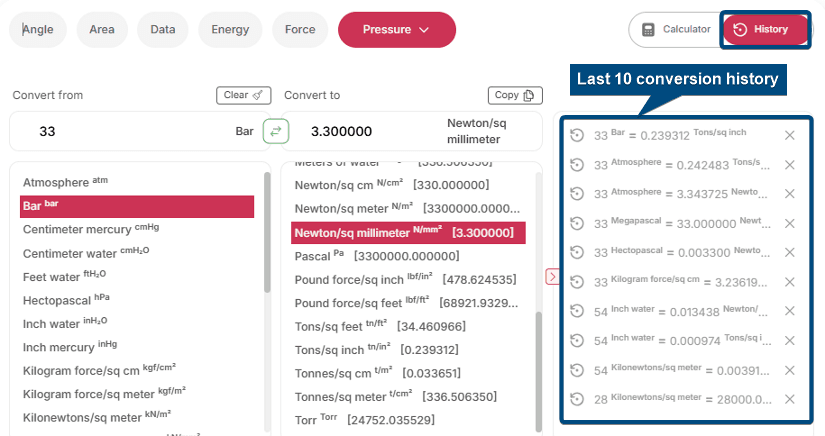
Auto-Saved Conversion History
Doing several conversions in a row makes it easy to lose track of previous results. Re-entering data manually can be a hassle and lead to errors.That’s why our calculator has an auto-saved conversion history feature. It automatically saves your last 10 conversions, even if you close or refresh the page. Just click on the History tab to instantly pull up any past value. This keeps your calculations organized and speeds up your work.
Pressure Conversion Table
Click the button below to download the pressure conversion chart. This chart provides conversion factors for all your pressure calculations.2 Examples of Conversion with Our Pressure Converter
To convert pressure measurements accurately, multiply the source value by the appropriate conversion factor found in the Pressure Conversion Chart above. The formula is simple:Converted Value = Conversion Factor × Value of Source Unit
Here are two quick examples of pressure conversion:
Atmospheres (atm) to Pascals (Pa) Conversion
To convert atm to Pa, multiply the atm value by 101325. For example, to convert 2 atm to pascals:2 × 101325 = 202650 Pa
%20and%20Pascals%20(Pa).png&w=3840&q=75)
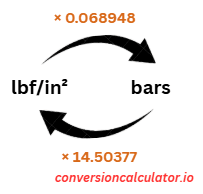
Pounds force/square inch (lbf/in² or psi) to Bars (bar) Conversion
To convert lbf/in² or psi to bars, multiply the lbf/in² value by 0.068948. For example, to convert 50 psi to bars:50 × 0.068948 = 3.4474 bar